As discussed in last post, In this section we will see configuration examples for 802.1x for Maipu routers and Switches, Here I covered Client base authentication, Mac base authentication, Radius based authentication.
Device Used - MP 1800 series
Let's see Client base authentication scenario -
802.1X Client Authentication
Topology Details
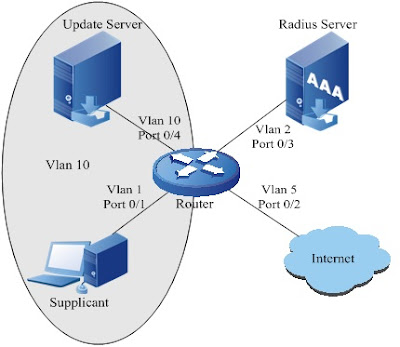
As shown in diagram, one user is connected to Port 0/1 of the device. The device manager of the device hopes to perform the 802.1X authentication for the user access on the port, so as to control the access for Internet.
Requirements:
- During the authentication, use the Radius authentication mode (the keys of the device and server are both set as maipu).
- When the user does not pass the authentication, he can access the Update Server (Update Server is in Vlan 10).
- After passing the authentication, the user can access Internet (the port of the device connected to Internet is in VLAN 5).
- After the user passes the authentication, the other users on the port can access Internet without authentication.
Topology
802.1x configuration diagram
Description
A host accesses the network via 802.1X authentication. The authentication server is a radius server. The accessed port 0/1 of the client host (Supplicant) is in the VLAN 1; the authentication server is in the VLAN 2; the Update Server is used for downloading and upgrading the client software, is in the VLAN 10; the port 0/2 connects to Internet of the switch is in the VLAN 5.
Configuration-
|
Command | Description |
| router#conf terminal | Enter the configuration mode |
| router(config)#aaa new-model | Enable the AAA mode |
| router(config)#aaa authentication connection default radius | Configure AAA as the radius authentication mode |
| router(config)#radius-server host 128.255.42.1 key maipu | Configure the radius server address and key |
| router(config)#vlan 2 | Create vlan2 |
| router(config-vlan2)#exit | Exit the vlan configuration mode |
| router(config)#port 0/3 | Enter the port configuration mode |
| router(config-port-0/3)#port access vlan 2 | Add port 0/3 into VLAN 2 |
| router(config-port-0/3)#exit | Exit the port configuration mode |
| router(config)#interface vlan 2 | Enter the interface configuration mode |
| router(config-if-vlan2)#ip address 128.255.42.10 255.255.255.0 | Configure the address information of vlan2 interface |
| router(config-if-vlan2)#exit | Exit the interface configuration mode |
| router(config)#vlan 5 | Create vlan5 |
| router(config-vlan5)#exit | Exit the vlan configuration mode |
| router(config)#port 0/2 | Enter the port configuration mode |
| router(config-port-0/2)#port access vlan 5 | Add port 0/2 into VLAN 5 |
| router(config-port-0/2)#exit | Exit the port configuration mode |
| router(config)#vlan 10 | Create vlan 10 |
| router(config-vlan10)#exit | Exit the vlan configuration mode |
| router(config)#port 0/4 | Enter the port configuration mode |
| router(config-port-0/4)#port access vlan 10 | Add port 0/4 into vlan10 |
| router(config-port-0/4)#port 0/1 | Switch to port 0/1 configuration mode |
| router(config-port-0/1)#dot1x port-control enable | Enable the 802.1X authentication mode |
| router(config-port-0/1)#dot1x port-method portbased | Configure the port-based access control mode |
| router(config-port-0/1)#dot1x guest-vlan 10 | Configure vlan10 as guest vlan |
| router(config-port-0/1)#exit | Exit the port configuration |
| router(config)# |
|
802.1x configuration diagram
The port 0/1 is added into the Guest VLAN, and the supplicant and update server are both in VLAN10 at the time. The supplicant can access the Update Server and download the 802.1X client:
802.1x configuration diagram
When the user passes the authentication and is online, the authentication server assigns VLAN 5. Right now the supplicant and port 0/2 are both in VLAN 5, and the Supplicant can access the Internet.
Let’s have look for MAC base authentication -
MAC Address Authentication
Local Authentication
Topology Details -
As shown in diagram, one user is connected to port 0/0 of the device. The manager of the device hopes to perform the MAC address authentication for the user access on the port, so as to control the access for Internet.
Requirements:
- The device detects whether the user is offline with an interval of 120s.
- After the user authentication fails, the authentication can be performed again only after 5 minutes.
- During the authentication, use the local authentication mode.
- Use the source MAC of the user as the user name and password and the MAC address uses the hyphen “-“.
Topology
Local authentication mode
Configuration
| Command | Description |
| router#conf terminal | Enter the configuration mode |
| router(config)#user 00-01-7a-22-22-33 password 0 00-01-7a-22-22-33 | Configure the local user; the user name and password are the MAC address of the user to be connected 00-01-7a-22-22-33 |
| router(config)#aaa new-model | Enable the AAA mode |
| router(config)#aaa authentication connection default local | Configure the AAA local authentication mode |
| router(config)#port 0/0 | Enter the port configuration mode |
| router(config-port-0/0)#dot1x timeout offline-detect 120 | Configure performing the offline detection for the user with an interval of 120s |
| router(config-port-0/0)#dot1x timeout quiet-period 300 | Configure the quiet time as 5 minutes (300s) after the user authentication fails |
| router(config-port-0/0)#dot1x mac-authentication enable | Enable the MAC authentication function on the port |
| router(config-port-0/0)#dot1x mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address with-hyphen | Configure the MAC authentication user name format: use the MAC information with hyphen “-“ as the use name and password (the option is the default configuration) |
| router(config-port-0/0)#exit | Exit the port configuration mode |
The show running-config command is used to view the current configuration information:
router#show running-config
Building Configuration...done
……
user 00-01-7a-22-22-33 password 0 00-01-7a-22-22-33
……
aaa new-model
aaa authentication connection default local
……
port 0/0
dot1x timeout offline-detect 120
dot1x timeout quiet-period 300
dot1x mac-authentication enable
exit
……
Let’s have look for Radius Authentication -
RADIUS Authentication
Topology Details
As shown in diagram, one user is connected to port 0/0 of the device. The device manager hopes to perform the MAC address authentication for the user access on the port, so as to control the access for Internet.
Requirements:
- The device detects whether the user is offline with an interval of 120s.
- After the user authentication fails, the authentication can be performed again only after 5 minutes.
- During the authentication, use the Radius authentication mode (set the keys of the device and server as maipu).
- During the authentication, adopt the fixed user name format; the user name is abcd and the password is 1234.
Topology
Radius authentication mode
Configuration
Note-
When using RADIUS authentication, ensure that the route between the device and the RADIUS is available and add the user name and password successfully on the RADIUS server.
| Command |
Description |
| router#conf terminal | Enter the configuration mode |
| router(config)#aaa new-model | Enable the AAA mode |
| router(config)#aaa authentication connection default radius | Configure AAA as the radius authentication mode |
| router(config)#radius-server host 128.255.42.1 key maipu | Configure the Radius server address and key |
| router(config)#interface vlan 1 | Enter the interface configuration mode |
| router(config-if-vlan1)#ip address 128.255.42.10 255.255.255.0 | Configure the address information of vlan1 interface |
| router(config-if-vlan1)#exit | Exit the interface configuration mode |
| router(config)#port 0/0 | Enter the port configuration mode |
| router(config-port-0/0)#dot1x timeout offline-detect 120 | Configure performing the offline detection for the user with an interval of 120 |
| router(config-port-0/0)#dot1x timeout quiet-period 300 | Configure the quiet time as 5 minutes after the user authentication fails (300s) |
| router(config-port-0/0)#dot1x mac-authentication enable | Enable the port MAC authentication function |
| router(config-port-0/0)#dot1x mac-authentication user-name-format fixed account abcd password 1234 | Configure the MAC authentication user name format: fixed user name format; the user name is abcd and the password is 1234 |
| router(config-port-0/0)#exit | Exit the port configuration mode |
The show running-config command can be used to view the current configuration information:
router#show running-config
Building Configuration...done
……
aaa new-model
aaa authentication connection default radius
……
port 0/0
dot1x timeout offline-detect 120
dot1x timeout quiet-period 300
dot1x mac-authentication enable
dot1x mac-authentication user-name-format fixed account abcd password 1234
exit
……
interface vlan1
ip address 128.255.42.10 255.255.255.0
exit
radius-server host 128.255.42.1 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 priority 0 key maipu
……
Monitoring Commands
|
Command |
Description |
| show dot1x | Display the default parameter information of 802.1x |
| show dot1x statistic | Display the 802.1x statistics information |
| show dot1x user {port|link-aggregation|summary } | Display the 802.1x user information of the specified port. If the port is not specified, display all user information. If summary is input, display the user quantity information. |
| show dot1x config {port|link-aggregation} | Display the 802.1x configuration of a specified port; if no port is specified, display the 802.1x configuration of all ports (the ports which are not configured with any 802.1x item are not displayed) |
For environment and configuration, refer to client base authentication
router#show dot1x user
Displayed result:
NO. VLAN MAC_ADDRESS PORT NAME STATUS IP_ADDRESS USERTYPE USERNAME
---- ---- -------------- ------------------- ------------- --------------- -------- --------
1 10 0005.5de4.0e25 port 0/1 Unauthorized 128.255.42.111 DOT1X abcd
Total: 1 Authorized: 0 Unauthorized: 1 Unknown: 0
Description and analysis:
No: user serial number
VLAN: the VLAN of the user port
MAC_ADDRESS: user MAC address
PORT NAME: port name
STATUS: user authorization status
IP_ADDRESS: user IP address
USERTYPE: the user type (DOT1X user or MAC authentication user)
USERNAME: user name
Debug Command
View the user login authentication information via the command debug dot1x all.
Hope this configuration will help you for 802.1x configurations.
For any queries and feedback, Plz put comment with Name and mail id . you can use Name/URL option in profile ...
For any comments and feedback.Plz comment with your mail and Name, you can use Name/URL option in profile.













